Gitpaste-12, a botnet worm that was first seen in October this year has now evolved with new features. As researchers detected, Gitpaste-12’s new iteration has tools to exploit 31 vulnerabilities, targeting Linux, IoT, and Android tools. Some of the exploits include open-source tools, and it’s reported to infect over 100 devices already.
New Botnet Worm Infecting Open-source Tools
Gitpaste-12 was named after the botnet worm spreading through GitHub repositories, and is using Pastebin to host its malicious payloads. This was first discovered in October this year, where it came with 12 known exploits.
And now, it’s reported to have come with 31 exploits, attacking Android and open-source tools, IoT, and Linux devices.
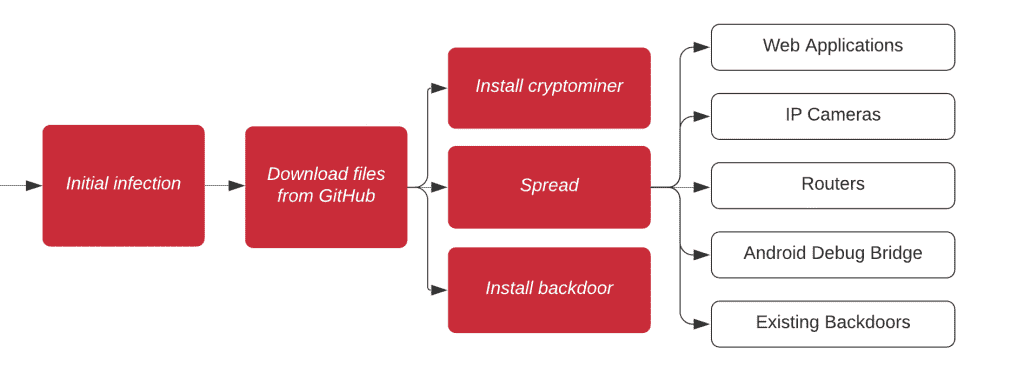
As documented by the Juniper Threat Labs, this latest iteration of Gitpaste-12 found on a different GitHub repository with just three files initially. These included a Linux cryptocurrency miner, a passwords list for brute-force attack, and a Python 3.9 interpreter with an unknown cause.
Later, more exploits were added to the Gitpaste-12. These include a Linux exploit called UPX pack for privilege escalation and a configuration file as “config.json” for mining Monero cryptocurrency. Authors have been minting coins to the same Monero address as Gitpaste-12’s first iteration.
It’s said that Gitpaste-12 starts with downloading a payload from its repository and makes a backdoor and a cryptocurrency miner in the host machine. Later, it spreads further to infect the connected Android devices through Android Debug Bridge and IoT devices like routers and cameras.
Researchers listed out all the 31 exploits that Gitpaste-12 attacks on, and these include some open-source tools like mongo-express, CutePHP, FuelCMS, and JBoss Seam 2.
While it’s unknown how successful this new botnet worm is, since it uses untraceable Monero cryptocurrency, researchers said they had identified over 100 distinct hosts. While we see how Gitpaste-12 evolves, researchers have listed the IOCs, identifiers, and all 31 exploits. Check out;
https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2010-1871
https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2010-3313
https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2014-8361
https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-17215
https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-17562
https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-11511
https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2019-10758
https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2019-11447
https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2019-19509
https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2020-5902
https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2020-8816
https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2020-10987
https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2020-17463
https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2020-17496
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/37474
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/40500
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/45135
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/45161
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/46542
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/48225
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/48358
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/48676
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/48734
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/48737
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/48743
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/48751
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/48758
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/48771
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/48775



