If you are a gamer, you might have probably heard about Steam or have it on your Windows 11 PC. Steam is one of the best platforms for gamers for playing games. There have been various improvements to make more features available to Steam Client and to make it robust. Though the platform is robust, that does not mean you may never expect to face any problems with it.
One such issue that users have reported facing with Steam on their Windows PC is the Steam Client WebHelper High CPU Usage. Steam Client WebHelper helps you view the Steam Store, Game library, and the community.
Also Read- Fix YouTube Audio Stuttering in Chrome on Windows
Fix Steam Client WebHelper High CPU Usage
Facing Steam Client WebHelper High CPU Usage on your Windows PC? Given below are the steps to help fix the issue you have been facing-
1. Disable Steam Overlay
The very first thing that you can try doing is disable Steam Overlay. To do so, follow the steps-
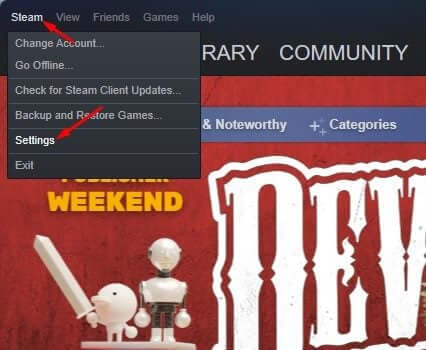
- Open Steam Client on your PC.
- Click on Steam in the top left corner and click on Settings.
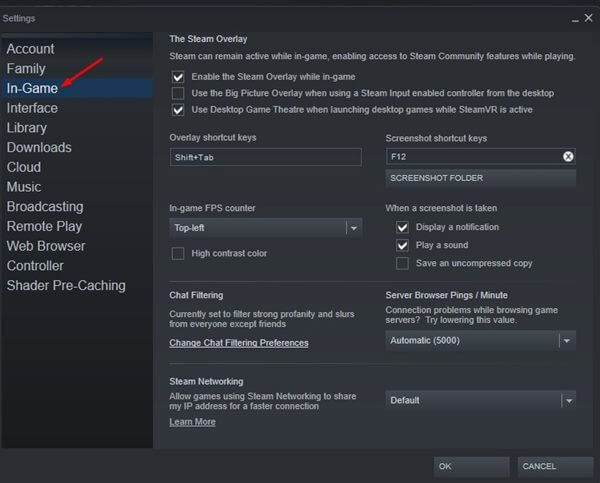
- Head to the In-Game option on the left side.
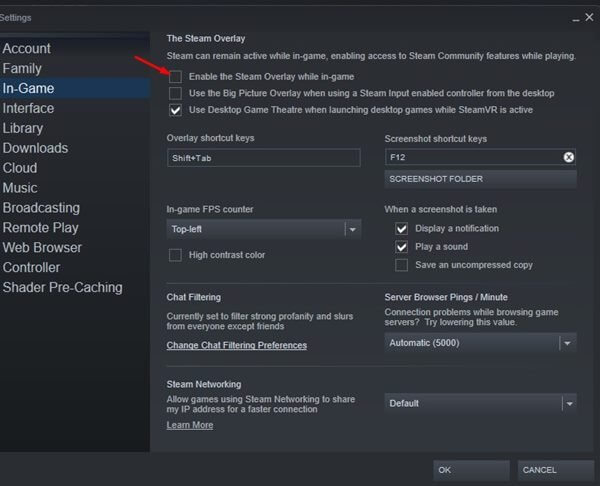
- Now on the right side, uncheck the checkbox for Enable the Steam Overlay while in-game.’ Click on OK to save changes.
- Restart your Steam client to save the changes.
2. Disable Animated Avatars
When Steam Client fails to load the Animated Avatar, you may face this issue. To disable animated avatars, follow the steps given below to disable animated avatars-
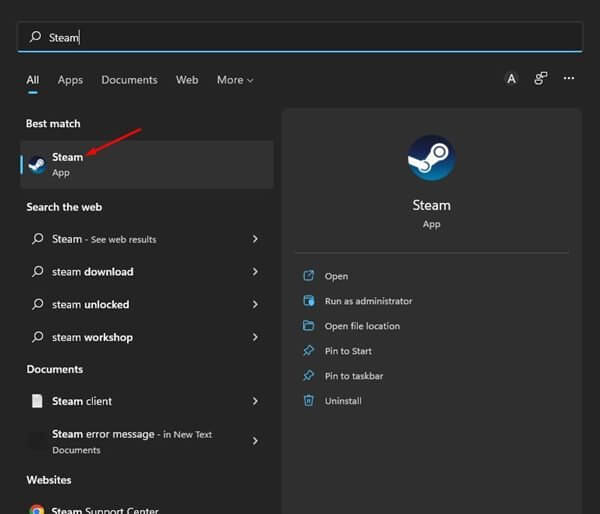
- Open Start Menu and search for and open Steam Desktop Client.
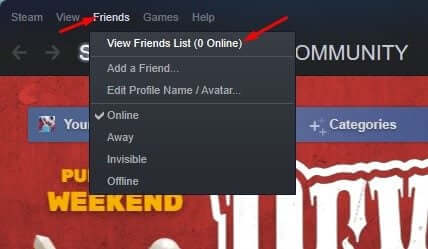
- Click on the Friends tab here, and then click on View Friends List.
- Next, click on the Settings (gear) icon.
- Turn off the toggle for the Enable Animated Avatars & Animated Avatar Frames in your Friends List and Chat.
- Restart the Steam Client and then check if you still face the issue or not.
3. Turn Off Other Visual Elements
The very next troubleshooting step to follow is disabling other visual elements of Steam Client. To do so, follow the steps given below-
- Open Steam Desktop Client on your PC.
- Here, click on the Steam tab and then on Settings.
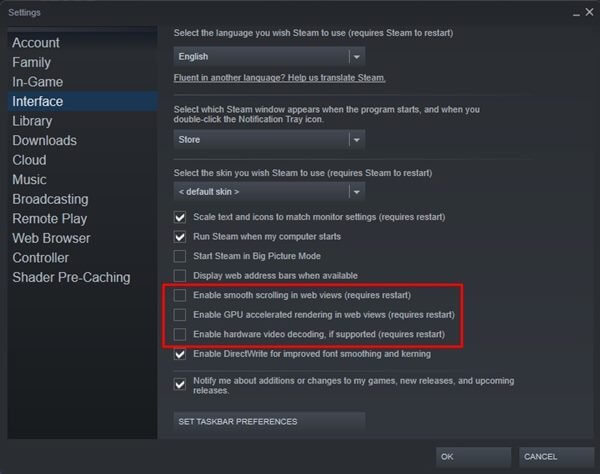
- Head to the Interface tab, and then uncheck the checkbox for the following options-
- Enable smooth scrolling in web views
- Enable GPU accelerated rendering in web views
- Enable hardware video decoding
- Once done, click on OK and check if you still encounter the issue or not.
4. End Steam Client WebHelper
If you still face the Steam Client WebHelper High CPU Usage on Windows, then you should end the Steam Client WebHelper and run Steam Client without it. To do so, follow the steps given below-
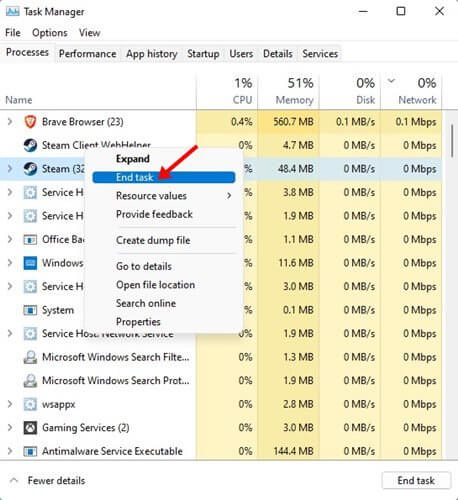
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc key combo to open the Task Manager.
- Click on the Process tab, and search for all the processes related to Steam Client. End all these Steam Client Processes.
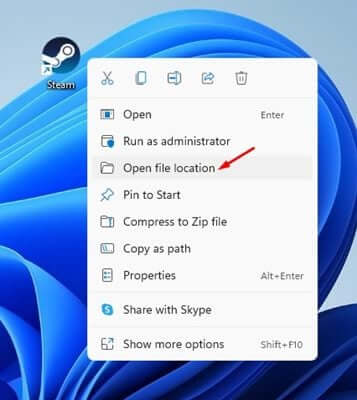
- On your Desktop, right-click on the Steam Client Desktop icon, and click on Open File Location.
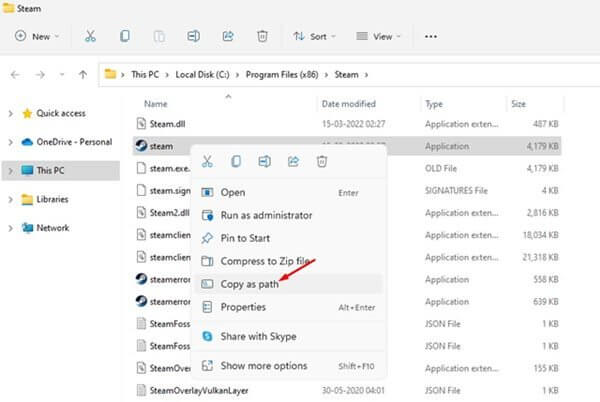
- Here, right-click on the Steam.exe file and click on Copy as path.
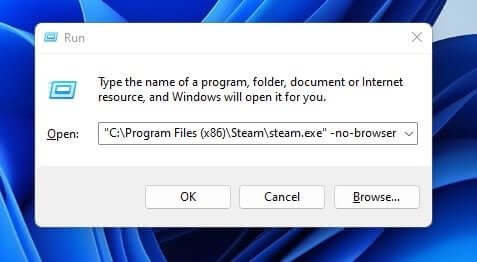
- Now open the Run Dialog Box, paste the path you copied and click on OK.
- Doing so will open the Steam Desktop Client without the WebHelper, and you should no longer face the issue.
5. Reinstall Steam Client
The last option to resort to this issue would be to reinstall Steam Client. Go for this troubleshooting step only if none of the above steps helped you fix the issue. To reinstall Steam Client, follow the steps given below-
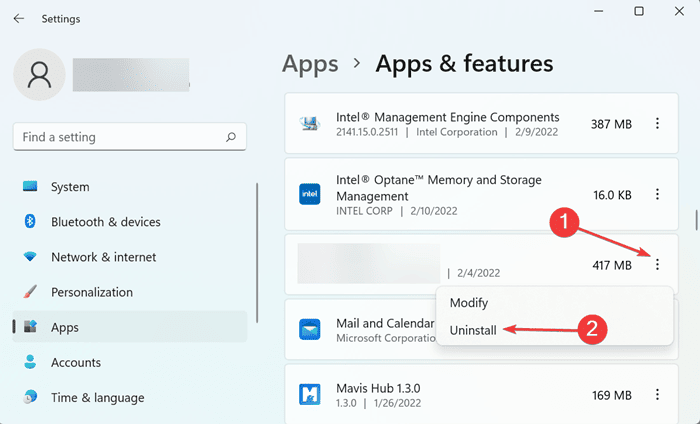
- Open the Settings app by pressing the Windows + I key combo.
- Head to the Apps tab, and then click on Apps & Features.
- Search for Steam Client Desktop, click on three ellipses next to it, and then on Uninstall. Confirm uninstall the application.
- Once done, download and install the Steam Client Desktop.
- Open Steam Client Desktop after reinstalling it and log in with your account. You should now no longer face the issue.
Bottom Line
These were the five troubleshooting steps to help fix Steam Client WebHelper High CPU Usage on Windows PC. Due to the high CPU usage of the WebHelper, your system may crash or start to slow down. Following the above steps, you will be able to fix the issue you will be facing.